Helicobacter pylori (Hp) is a kind of micro-anaerobic bacteria with spiral morphology, which requires harsh growth conditions, but can survive successfully in the human stomach. Since the first successful isolation of Helicobacter pylori from gastric mucosal biopsy tissue of patients with chronic active gastritis in 1982, it has attracted wide attention in the medical community. It is not only the only known microbial species that can survive in the human stomach, but also a carcinogen listed by the International Agency for Research on Cancer of the World Health Organization. Therefore, in-depth study and understanding of the pathogenesis of Helicobacter pylori is of great significance for the prevention and control of related diseases.
Source:sohu.com
1、Pathogenesis of Helicobacter pylori
Helicobacter pylori is transmitted through diet, is highly infectious, and has been classified as a group I carcinogen by the World Health Organization. After infection, it can cause active inflammation of gastric mucosa. On the basis of chronic inflammation, some patients may also suffer from a series of diseases such as peptic ulcer and gastric cancer. The survival and pathogenic mechanism of Helicobacter pylori in the stomach is an important topic in medical research.
Source: 699pic.com
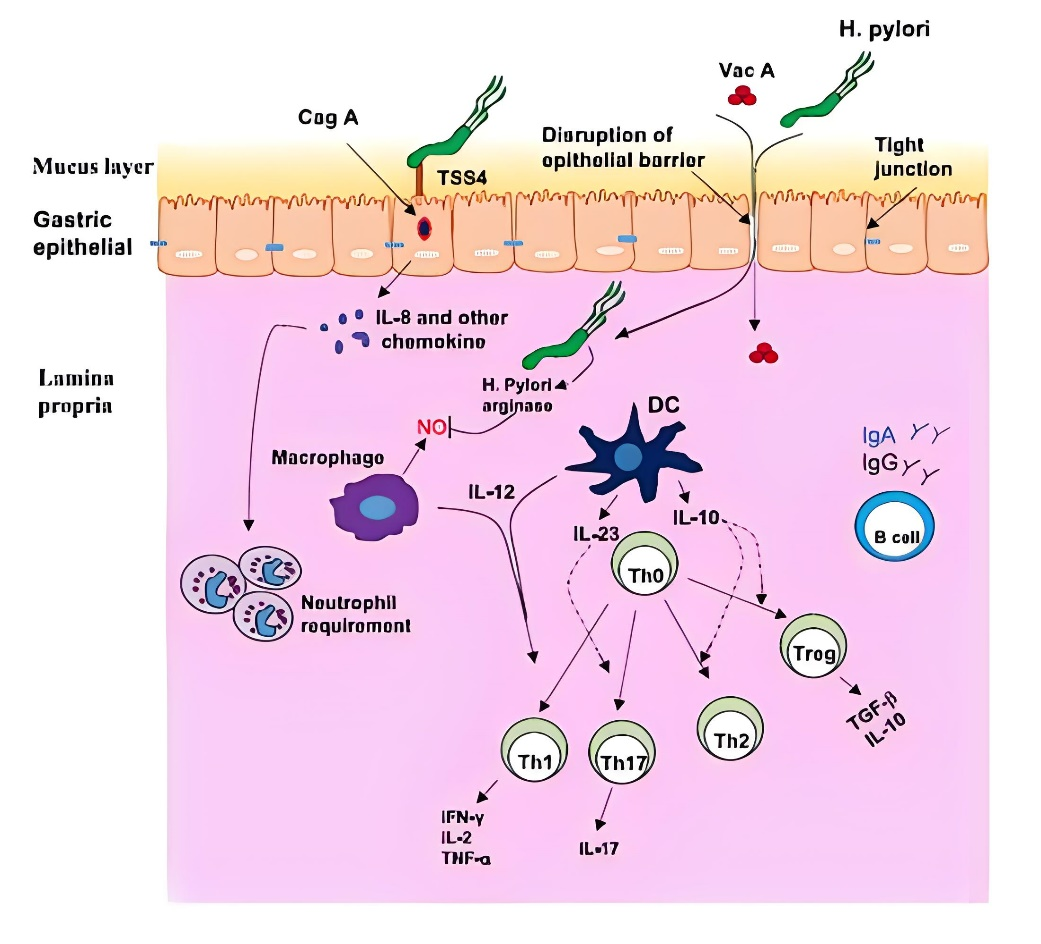
First of all, Helicobacter pylori can survive in gastric acid environment, mainly depending on its unique urease, which is a nickel-containing metalloenzyme composed of two subunits (UreA and UreB), which can decompose urea to produce ammonia to neutralize gastric acid and form a microenvironment conducive to its survival. Secondly, Helicobacter pylori can produce a variety of virulence factors, such as Caga protein and Vaca protein, which can destroy the gastric mucosal barrier, cause inflammation, and even lead to cell damage and canceration. The Expert Consensus on Eradication of Helicobacter Pylori and Prevention and Control of Gastric Cancer in China in 2019 points out that the detection of serum antibodies to cytotoxin-related gene A (CagA) and vacuolating cytotoxin A (VacA) of Hp can be used for Hp screening, and eradication is recommended for strains with positive Hp virulence. Hp can be divided into type I and type II according to whether it contains the cytotoxin-associated pathogenicity gene cluster (Cag-PAI) and vacuolating cytotoxin antibody typing. Type I produces cytotoxins CagA and VacA with strong toxicity, which can cause chronic gastritis, peptic ulcer and gastric lymphoma, and is related to gastric cancer. Type II does not produce cytotoxin CagA and VacA, and the antibodies of the two toxins are negative, with low virulence, which often causes chronic superficial gastritis. Antibody which do not contain CagA and VacA 2 toxins and contain any one of UreA and UreB are HpII.
In addition, the interaction between Helicobacter pylori and the host immune system is also an important part of its pathogenic mechanism. Although the body will have a strong immune response to Helicobacter pylori infection, due to the escape mechanism of Helicobacter pylori, it can continue to survive and cause disease under immune pressure. At present, it is still a hot spot to study the mechanism of how Helicobacter pylori escapes from immune effector molecules and how to induce host immune protection by vaccine.
Source:zhihu.com
2、Prevention and control strategies of Helicobacter pylori
At present, the route of Hp infection is not yet clear. The recognized routes of Hp transmission are intrafamilial transmission and fecal-oral transmission. In addition, iatrogenic transmission, oral-oral transmission and sewage transmission may also be the routes of human infection with Hp. Hp infection has posed a serious threat to human life and health. In view of the susceptibility of Hp and its high harmfulness to human health, as well as the incomplete prevention due to the uncertain transmission route, scholars at home and abroad are trying to find a highly sensitive and specific method to detect Hp in order to achieve the purpose of “early detection and early treatment”. At present, there are many methods to detect HP infection, including invasive and non-invasive screening methods.
Hp invasive detection method refers to the process of medical instruments invading the body, which mainly includes the visual examination of the internal morphology of the stomach after the gastroscope enters the stomach and the in vitro examination after the mucosal tissue is clipped by the sampling forceps, and ultimately achieves the purpose of detecting the existence of Hp. Endoscopy, histopathology, immunohistochemistry (IHC), isolation and culture, and rapid urease test (RUT) are the main methods to detect Hp invasion.
Source: sohu.com
Hp non-invasive detection methods: Hp non-invasive detection methods use specimens that are nearly non-invasive and easy to obtain for patients (such as exhaled breath, saliva, dental plaque, urine, feces, serum, etc.). At present, non-invasive detection methods for Hp mainly include urease detection method, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (enzyme linked immunosorbent assay, ELISA), and immunochromatography assay. ICA, immunoblotting test (IBT) and polymerase chain reaction (PCR).
Source: thepaper.cn
3、 Product Introduction
Compared with invasive detection methods, non-invasive detection methods are widely accepted by patients because of their many advantages, such as non-invasive, comfortable, safe, convenient, rapid, cost-effective, repeatable, and conducive to large-scale screening.
There are two types of HP diagnostic kits independently developed by our company. One is a rapid detection card for in vitro qualitative detection of Helicobacter pylori antibody in human blood/serum/plasma samples. This product is based on the double antigen sandwich method to rapidly detect HP antibody. The second is a rapid detection card for in vitro qualitative detection of Helicobacter pylori antigen in human stool samples. This product is based on the double antibody sandwich method to rapidly detect HP antigen. Both products use colloidal gold immunochromatography technology, which is simple, convenient and accurate, more conducive to the protection of personal privacy, and the results can be obtained in 15 minutes.
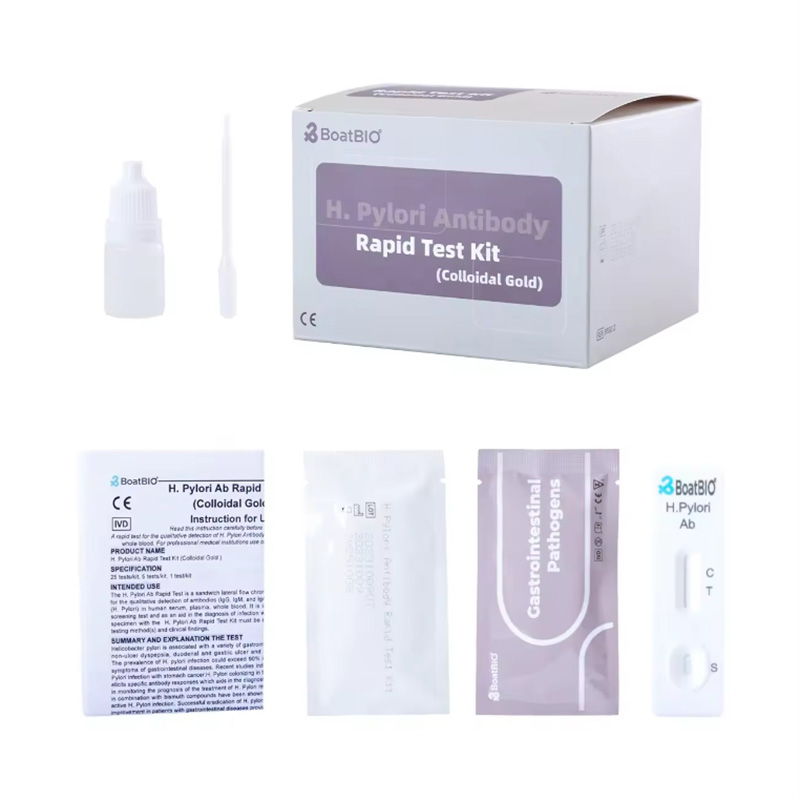
4. Who needs to be tested for Helicobacter pylori?
People with frequent epigastric fullness, discomfort or pain after normal meals, or with other dyspeptic symptoms, such as belching, abdominal distension, acid reflux and loss of appetite, or with recurrent severe abdominal pain, need to be tested for Hp, but they need to stop using proton pump inhibitors and potassium ion competitive acid blockers for at least 2 weeks before testing, and bismuth and antibiotics for at least 4 weeks to reduce false negative.
Patients with no family history of gastric cancer and no dyspepsia may not be routinely tested for Hp.
5、Summary and Prospect
Helicobacter pylori is an important pathogen of gastric diseases, and its research and prevention are of great significance to global public health. With the development of science and technology, the diagnosis and treatment methods of Hp are constantly updated, but they are still facing challenges such as the rise of drug resistance and the fluctuation of eradication success rate. In the future, it is necessary to further optimize the diagnosis and treatment strategies, develop new anti-Hp drugs and vaccines, and strengthen public health education and infection control in order to reduce the global burden of Hp-related diseases.





